Will the World Reach its Green Energy Tipping Point in 2023?

Entering the year of 2023, the world is on the edge of a green energy tipping point.
In 2010, solar and wind power made up just 1.7% of global electricity generation. But since then, the industry has grown rapidly, with solar and wind producing 8.7% of the world’s electricity in 2020. A variety of factors, including green energy policies and technology investments, continue to drive momentum. The International Energy Agency (IEA) Renewables 2022 report analyzes the progress of the green energy industry made over the past year and forecasts that renewables will experience immense growth in the near future, becoming the largest source of global electricity generation by 2025. As an illustration of the massive changes expected to come soon, IEA Executive Director Fatih Birol stated, “The world is set to add as much renewable power in the next five years as it did in the previous 20 years.”
What has spurred this sudden shift in the energy industry? A variety of factors including changes in supply chains, material costs, geopolitical alignments, and government-level policies to address climate change have contributed, but the momentum would not be possible without the massive investment and bold moves of the business sector.
Hanwha has been leading the charge in the transition to green energy around the world. Its dedication to expanding clean energy can be seen in its latest investment in solar energy in the U.S. state of Georgia: the single largest investment in solar energy in the country to date, and a move that President Biden called, “a win for workers, consumers and our climate.”
With a robust portfolio of solar, wind and hydrogen solutions that continue to expand globally, Hanwha’s continued focus on sustainability and clean energy investments are helping the world along the path to reaching net zero targets by 2050.

2023: The Year of Renewable Growth
The IEA’s report details remarkable progress for the state of renewables going forward, especially within the next five years.
Overall, global renewable energy capacity is expected to grow by 2,400 gigawatts, an amount equivalent to China’s entire energy capacity. Solar energy is the biggest leader in this regard, with global solar PV capacity predicted to overtake coal by 2027, becoming the largest source of electricity generation in the world. Wind power is set to experience immense growth as well, almost doubling in capacity over the same period.
Emerging forms of green energy are also set to continue expanding. Specifically, green hydrogen will experience growth as countries continue to invest in the technology and build out hydrogen infrastructure. Over the next five years, global renewable capacity dedicated to hydrogen production is set to increase 100-fold. Expanding overall hydrogen production will help pave the way for green hydrogen technology to become more viable for future use in the manufacturing and transportation industries.
What accounts for this rise? Technological advancements have both improved efficiency and helped lower prices across the board. In addition, while previously solar panels were quite costly to manufacture due to labor and raw material costs, increased demand has brought down the cost of materials. This has raised both solar panel production and subsequently energy capacity, helping to further push solar panel prices down and expand solar energy deployment. Similarly, advancements in wind turbine technology and increased market competition have also made wind energy cheaper to install and use.
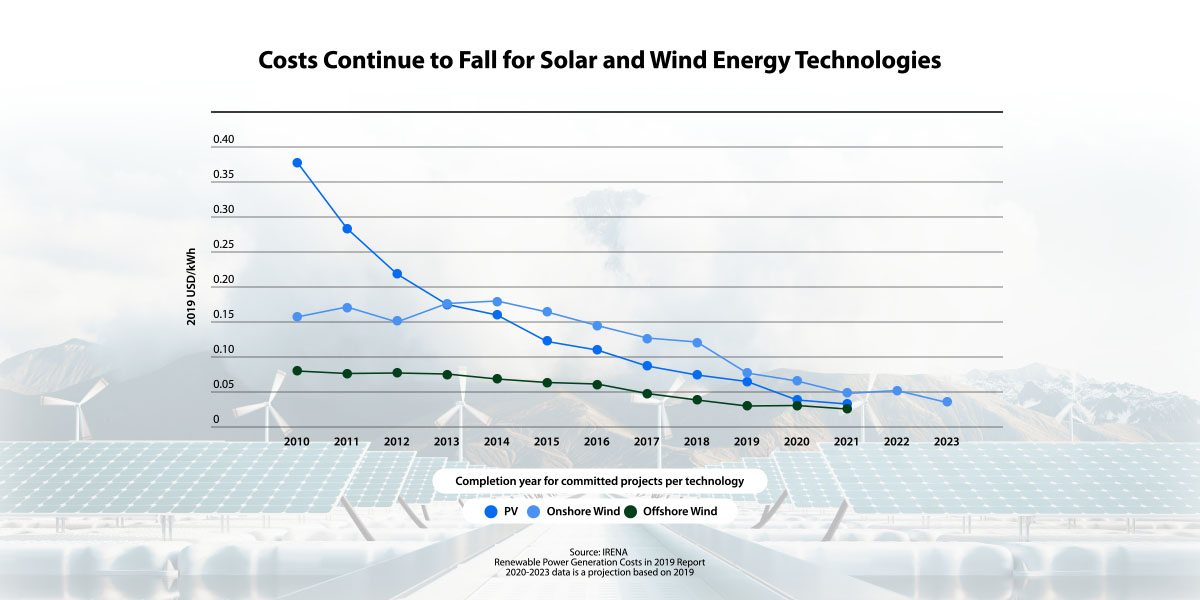
The IEA report argues that the fears over the stability of traditional energy supplies in early 2022 also opened the door for clean energy development, causing a sharp acceleration of clean energy adoption throughout the world. Inflated prices for traditional energy sources coupled with increased energy demand caused renewable prices to further drop and adoption to rise, especially in Europe. This trend is expected to continue, with low prices and concerns over climate change making renewable solutions an increasingly attractive option.
These trends all point to 2023 being a tipping point for the green energy industry, giving us hope that it may still be possible to curb the effects of global warming and keep global temperatures under the 1.5 degrees Celsius (2.7 degrees Fahrenheit) threshold. However, there’s still more work to be done in pushing forward towards a sustainability-driven future, made possible through continued clean energy development driven by companies like Hanwha and the cooperation of nations around the world.

Hanwha Solutions’ Qcells Division (Hanwha Qcells) Dalton Factory
Onwards and Upwards: Clean Energy Growth Going Forward
In order to continue expanding clean energy around the world, the IEA emphasizes that governmental and economic policy are the key. From improving production and storage infrastructure to further incentivizing clean energy development, the right policies can smooth the way for the energy transition by removing regulatory and logistical roadblocks and supporting investment where it’s needed the most. Better policy could help expand global clean energy capacity by almost 3,000 gigawatts, helping the Earth reach net zero targets even sooner.
Government policies are instrumental in furthering clean energy development across the world, helping to lower entry costs to the industry, expand technological development for clean energy and more. The EU’s new REPowerEU plan is expected to significantly scale up clean energy production. China has also set bold policy targets, with its new Five-Year-Plan stating a goal of 33% renewable consumption by 2025, leading the country to account for almost half of the renewable global capacity that will be added between 2022-2027. The U.S. Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) offers robust incentives to companies to pursue green energy development in the U.S., including Hanwha.
Before the IRA, uptake of solar energy in the U.S. was on the rise, but stalled owing to supply chain issues in 2021. Because solar supply chains are heavily concentrated in just a few countries, pandemic disruptions led to difficulty obtaining necessary materials on the global market and caused prices to rise. Diversifying material sourcing by expanding supply chains to other nations can both help reduce supply chain imbalances and ensure a smoother transition to clean energy. In recognition of this need, Hanwha is taking advantage of the incentives in the IRA to build out an end-to-end solar supply chain in the U.S., an initiative that will both expand the company’s development of solar energy and contribute to reinforcing the solidity of the global solar market.
Pioneering Progress with Bold Business Pursuits
Hanwha is making big moves to speed up the shift to a completely clean solar supply chain. Hanwha Solutions recently announced a groundbreaking plan to invest 2.5 billion USD to build a complete solar supply chain in the U.S. The new facility, which will be located in Cartersville, Georgia will be responsible for manufacturing three of the core parts needed for solar panels: ingots, wafers, and cells, as well as modules.

This investment will also help Hanwha expand operations at its current facility in Dalton, Georgia, increasing the current 1.7-gigawatt production to 5.1 gigawatts by the end of this year. With an additional 3.3 gigawatts from the new facility, the two facilities will be able to produce a total of 8.4 gigawatts, enough energy to power 1.3 million U.S. households for a year and equivalent to reducing 9.78 million metric tons of carbon emissions a year. With production at the facility set to begin in 2024, the new complex at Cartersville would bring Hanwha’s solar panel production capacity up to 60,000 per day. The facility will also help lower solar energy costs across the board, providing more consumers in the U.S., and around the world, with more affordable, sustainable energy.

Another way Hanwha is securing an Earth-friendly solar supply chain is with its acquisition of a major stake in REC Silicon, a major polysilicon producer. Through this venture, the company will be able to source clean polysilicon, the raw material necessary to create solar modules, from its plants in the U.S. REC Silicon is currently in the process of restarting production at its Moses Lake facility, with operations expected to resume at the end of 2023. The plant runs on hydropower-generated electricity, meaning the polysilicon it produces will be manufactured with ultra-low carbon emissions. With this clean polysilicon supply, Hanwha will be capable of producing solar panels from start to finish in the U.S., becoming the first to establish a complete solar value chain in North America.

Hanwha’s major steps towards becoming the first completely clean solar manufacturer in the U.S. have drawn attention from corporations around the world, including Microsoft. In another pioneering move, Hanwha Solutions recently announced that they have entered a strategic alliance with the tech giant to strengthen the renewable energy supply chain. Hanwha Qcells will collaborate with Microsoft in developing new solar projects while also supplying Microsoft’s solar project developers with more than 2.5 gigawatts of solar panels and related services. The unprecedented partnership further illustrates the IRA’s impact on driving the renewable energy transition forward as well as Hanwha’s position as the green energy provider of choice among major global brands.
Investments in solar energy are just one of the ways Hanwha is helping bring the world transition to clean energy closer to fruition. Hanwha is also working diligently to integrate sustainability into its businesses, developing clean energy and technologies for consumers around the globe.

Korean Prime Minister Han Duck-Soo Visits Hanwha Qcells, North America’s Largest Solar Manufacturer
Sustainability at the Forefront
Hanwha’s clean energy investments go beyond its solar projects in the U.S. Hanwha is actively investing in and developing various green energy technologies around the world — another crucial step in helping push the world over the green tipping point.
Hanwha has been pursuing clean energy development in the EU, helping to build out infrastructure and improve technology for the region. Hanwha Qcells is working to improve solar cell efficiency through its 14.5 million USD tandem cell R&D project with European research institutes, a move to help the EU reach its REPowerEU goals, but Hanwha’s efforts don’t stop there. Hanwha has also been taking steps to expand its wind power portfolio. Hanwha Solutions’ acquisition of RES France, which is now Q ENERGY France SAS, a subsidiary under Q ENERGY Solutions SE, was a monumental move in expanding its green energy businesses throughout Europe. Q ENERGY France and its sister subsidiary Q ENERGY Europe have been bringing green energy to Europe, including both wind and solar energy, and plan to continue expansion of this business on the continent going forward. Hanwha Corporation E&C Division also recently signed an MOU with Equinor, a Norwegian energy company, to build offshore wind plants in South Korea.

Windmills Operated by Q ENERGY in France
Pursuing development in emerging energy solutions helps diversify clean energy technology, and Hanwha is doing just that. Aside from its solar and wind businesses, Hanwha is also making an effort to further green hydrogen development to make the technology more viable for future widespread use. Researching and incorporating the use of green ammonia to produce clean hydrogen, developing more effective hydrogen storage technology and creating “hydrogen to gas turbine” (H2GT) technology are just some of the ways Hanwha is helping to build out hydrogen infrastructure to take advantage of hydrogen’s potential.
Green technology such as battery storage, which can store energy produced by wind or solar to provide stable energy supplies, is another essential part of the clean energy transition. This allows for storage of energy generated by renewable sources, making it possible to utilize technologies like wind and solar even in places where the wind doesn’t always blow or the sun doesn’t always shine. Accordingly, Hanwha has stepped up to the mark.
Hanwha Qcells has also helped European nations navigate energy shortages through its energy storage system (ESS) and heat pump partnership with Samsung, in addition to Hanwha Energy’s multiple ESS projects in Ireland to bring sustainable energy to the country. In the U.S., Hanwha recently signed an MOU with LG Energy Solution establishing a comprehensive battery partnership, which includes ESS and other clean tech energy solutions. With LG Energy Solution, Hanwha will work to develop an ESS facility and technology for battery manufacturing facilities. This is in addition to the seven planned ESS projects Hanwha Qcells is bringing to the state of Texas, which will provide a storage capacity of 2.4 gigawatt hours (GWh), equivalent to the power used by one million people in a day. With climate tech set to become a 1.4 trillion USD market within the next five years, Hanwha remains devoted to furthering green technological development through its various businesses.
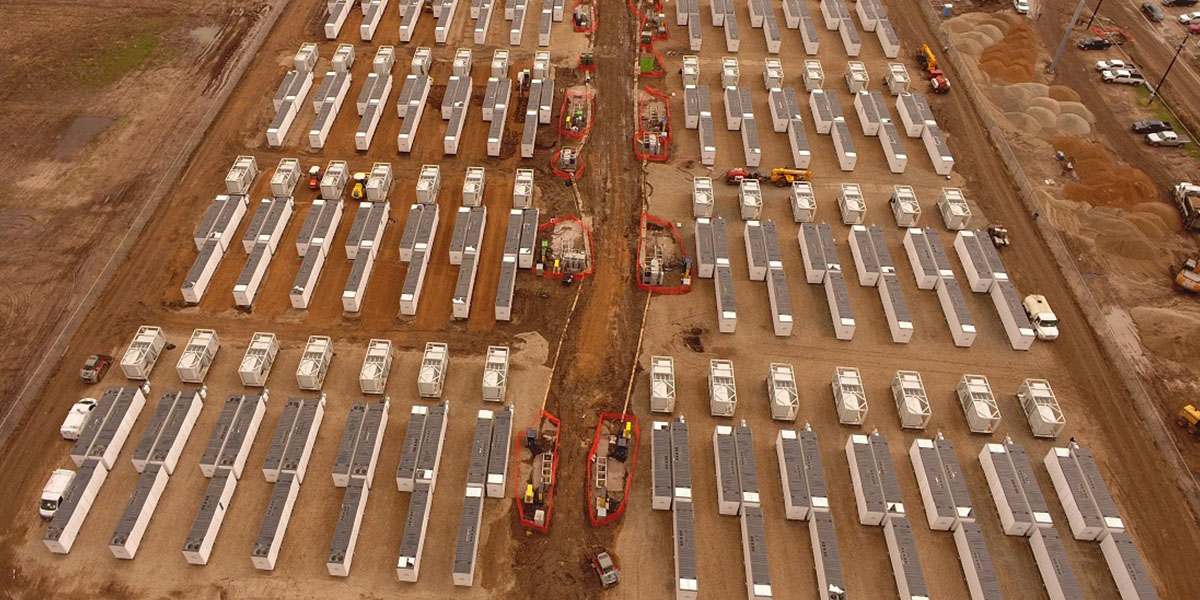

The Cunningham ESS Project Site in Texas
A Greener Future for All
The outlook on sustainable energy development for the near future highlights the positive changes being made throughout various industries. As such, 2023 is set to be an important year for sustainable development, setting the tone for clean energy growth for years to come. In order to further this growth with the ultimate goal of reaching net zero by 2050, nations and corporations around the world must continue to work together to combat global warming and create a sustainable future for all.
As the world increasingly turns to clean energy solutions, Hanwha is standing tall and working hard to achieve this shared global goal. Hanwha’s trailblazing work in sustainable energy will help push the world over the green tipping point, bringing the planet one step closer to a cleaner, brighter future.
Get the latest news about Hanwha, right in your inbox.
Fields marked with * are mandatory.
- Non-employee
- Employee




