Cobots in action: 4 sectors where collaborative robots are transforming the way we work

Collaborative robots, or cobots, are reshaping industries worldwide, working alongside humans in shared spaces and augmenting our capabilities with strength, precision, and advanced data processing. Designed to boost efficiency and safety, cobots have become vital tools in the evolving landscape of automation.
With the global robotics market projected to surpass $165 billion by 2028, cobots are expanding into a growing range of sectors. Initially confined to singular tasks like lifting and packaging, cobots are taking on more complex roles in industries like food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, health care, and the service sector. This evolution is being further propelled by sophisticated technologies like AI, sensors, and intuitive software, which enhance cobots’ adaptability.
Since introducing Korea’s first cobots in 2017, Hanwha Robotics has continued to refine its solutions to enhance human-robot collaboration. Certified for ISO Class 2 cleanroom environments, the Hanwha collaborative robot (HCR) series is suitable for use in industries such as food, manufacturing, shipbuilding, biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, and semiconductors. In this article, we will explore how cobots are changing the landscape of work and automation across four key sectors, examining the features that make them uniquely suited for these roles.

The next frontier in food tech
Amid global trends like rising consumption, stringent food safety regulations, and increasing demands for worker safety, robots are taking on important roles in the food and service industry, from delivering meals to tables to transporting orders around town.
Equipped with diverse attachments and vision technologies, cobots excel in precise applications like food processing, portioning, and packaging, while advanced software and sensors ensure safe operation without traditional safety barriers, making it possible for humans to work in close proximity.
Cobots are also easily programmable and portable, allowing them to streamline operations, mitigate contamination risks, minimize human error and ergonomic injuries, and uphold consistent quality, product safety, and compliance with regulatory standards.
Beyond basic automation tasks like slicing and cooking, cobots also offer significant potential for innovation in food production, taking on more intricate applications such as preparing meals from scratch. Hanwha is actively tapping into these capabilities, with its cobots crafting pasta at Hanwha Foodtech’s Pasta X restaurant in Hannam, Seoul. Hanwha Foodtech also acquired the U.S.-based robot pizza brand Stellar Pizza, whose robots prepare pizzas and manage multiple orders simultaneously, delivering high-quality meals at scale. Driving these innovations, Hanwha Foodtech operates a 1,349-square-meter R&D center in Seongnam dedicated to developing kitchen automation technologies, modular systems, and robotics. The center also creates menus for brands like Pasta X, Taoyuan Style, and Pavilion, ensuring that cobots contribute to both operational efficiency and culinary creativity.
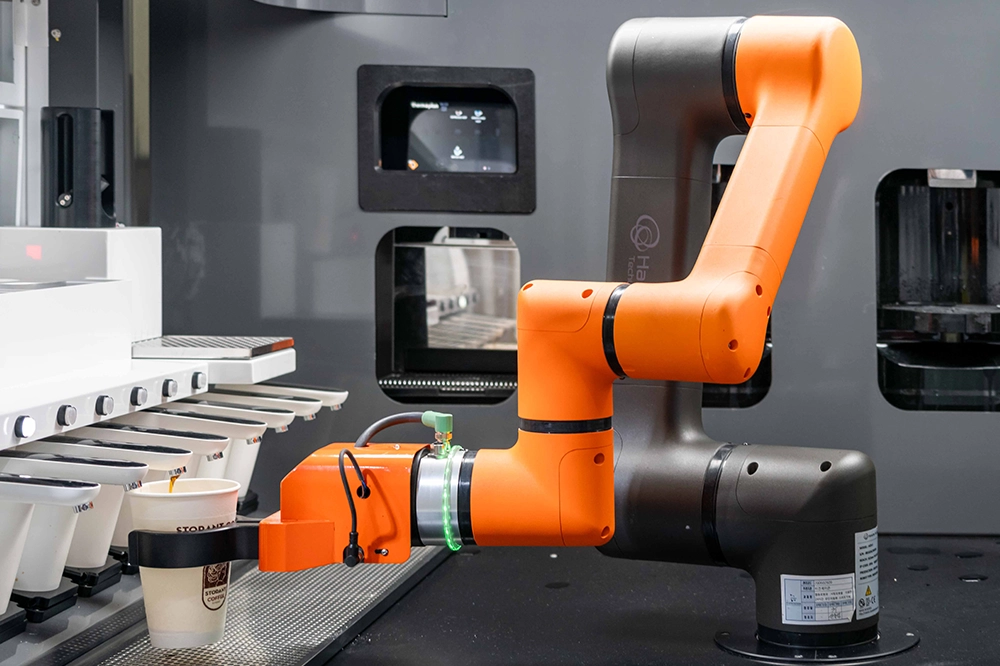

Hanwha Robotics' robot barista makes coffee
A new ally in pharmaceuticals, biotech, and health care
In pharmaceutical and biotech, cobots have become indispensable for tasks like dispensing, assembly, packaging, quality inspection, palletizing, and sorting — key areas where maintaining sterile environments and minimizing contamination risks are paramount. For example, cobots with attachments like grippers or suction cups can automate case packing, while 3D vision allows them to analyze 2D images to determine object shapes, supporting stacking operations and reducing worker exposure to hazardous tasks.
Furthermore, with growing demand for medical care, aging populations, rising health care costs, and a shortage of medical professionals, cobots are filling critical gaps in this sector. For instance, in surgical applications, cobots can perform minimally invasive procedures, enabling quicker patient recovery with fewer complications. They can also help patients perform specific movements post-surgery to support rehabilitation. Additionally, cobots are increasingly being used in telemedicine, enabling remote consultations and even minor surgeries — a game-changer in underserved or rural areas.

Smarter solutions for manufacturing
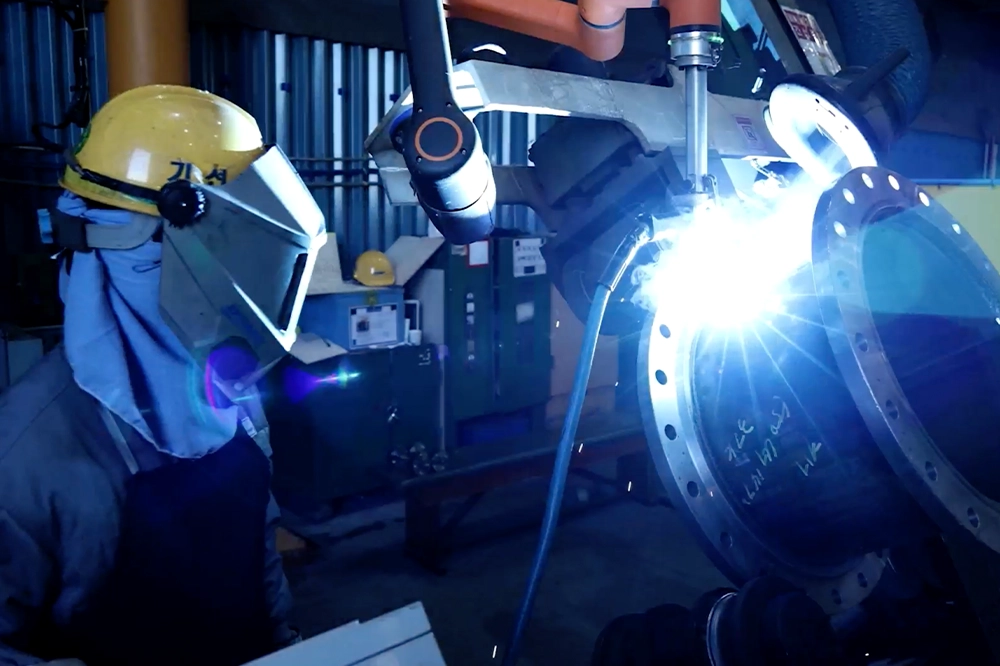
In the realm of manufacturing and automation, cobots are being employed in industries such as aerospace, semiconductors, shipbuilding, and automotive. Their intuitive programming and lightweight design make them ideal for tasks like welding, assembly, and loading. What’s more, cobots are capable of managing both large-payload, high-volume operations and smaller-payload, low-volume tasks, offering a flexible solution that saves space, energy, and resources.
Hanwha Robotics’ HCR series exemplifies these capabilities, including its latest model, the HCR-5A — a lightweight 10 kg cobot optimized for welding and other heavy-duty tasks. All HCR models have safety features like collision detection, which halts operations upon sensing human presence, reducing workplace accidents. Additionally, through the easy attachment of accessories like force torque sensors and grippers, cobots are versatile tools for pick-and-place operations, inspection, and mobile manipulation. Hanwha's cobots also leverage AI-driven 3D vision, visual safety tracking, and mobility packages, improving precision.
Building on these features, Hanwha’s cobots can be integrated with autonomous mobile robot (AMR) systems. For example, the HCR-5A can collaborate with AMRs like the turntable and pipe welding robot, which handles welding on moving objects, and the inkjet and laser marking robot, which marks objects at specified positions. Through various AMR-cobot integrations, manufacturers can adapt to increasingly complex production needs.
Hanwha recently showcased the safety features of its cobots and AMR systems at Welding Korea 2024 + Automation, underscoring their potential to transform modern manufacturing.
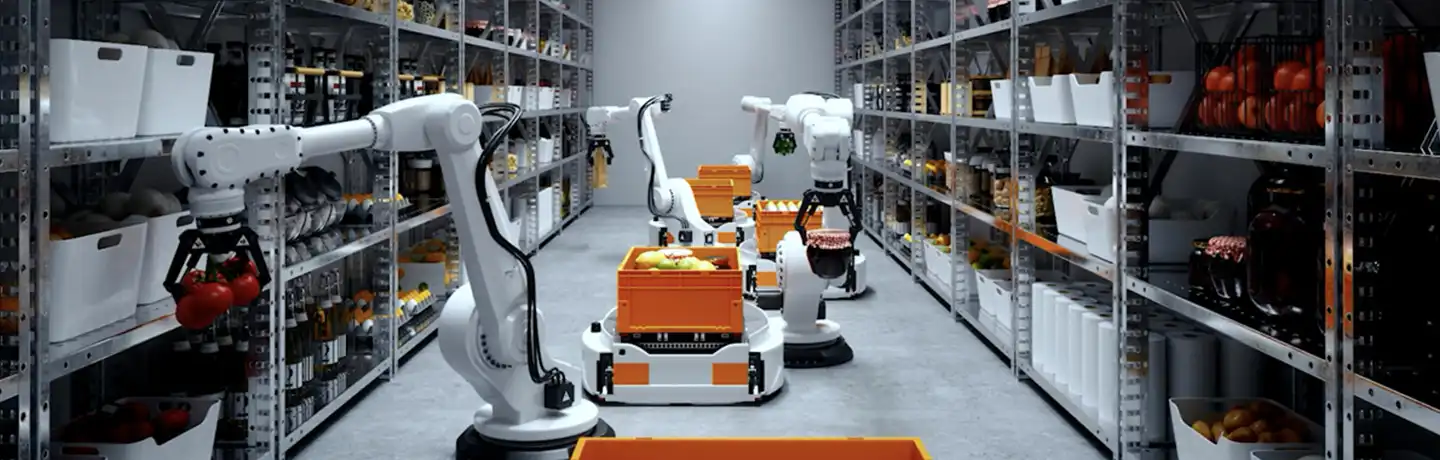
Streamlining logistics and warehouse operations
Logistics has long relied on robotics and automation technologies such as conveyor belts and scanners to streamline operations. However, recent advancements fueled by the e-commerce boom, labor shortages, and supply chain challenges have sparked a surge in robotics investment. With the rise of Industry 4.0 and smart factories, the integration of cobots with the Internet of Things, AI, and deep learning is set to revolutionize warehouse operations.
In this sector, cobots can be applied to tasks such as inventory management and transportation, while AI enables them to use computer vision and predictive analytics to navigate obstacles, recognize patterns, and adapt to dynamic environments. In smart factories, cobots often work in tandem with AMRs, enabling them to locate and pick objects quickly, navigate complex warehouse layouts, and deliver items to human workers. This integration bolsters productivity, with systems capable of increasing units picked per hour by up to threefold.
Hanwha Robotics’ HCR series cobots are well-suited for logistics applications, complying with strict safety standards. At Hanwha Aerospace’s Changwon smart factory, cobots utilize digital twin technology to provide comprehensive monitoring of inventory levels, automated guided vehicle (AGV) locations, production progress, and potential defects. This data, updated more than 20 times per second, is easily accessible through a computer interface. These capabilities lead to smoother workflows, enhanced operational efficiency, and increased throughput, allowing companies to react quickly to the ever-evolving demands of modern logistics.
Get the latest news about Hanwha, right in your inbox.
Fields marked with * are mandatory.
- Non-employee
- Employee






