How maintenance, repair, and overhaul is modernizing global defense capabilities
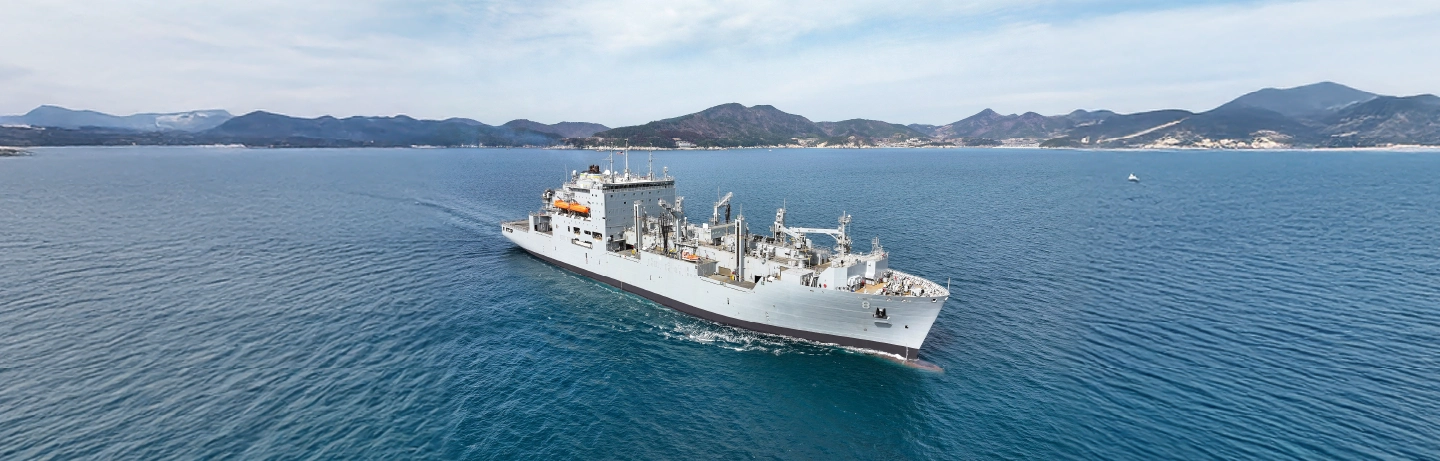

Amid a shifting defense landscape, nations are seeking to keep their assets robust, modernized, and resilient. Even the most advanced weapon systems cannot maintain their original performance without regular inspections and careful management, and governments are looking for ways to strengthen alliances and tackle shared security challenges. By addressing these key contemporary issues in defense, maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) has taken on a critical role in ensuring operational readiness.
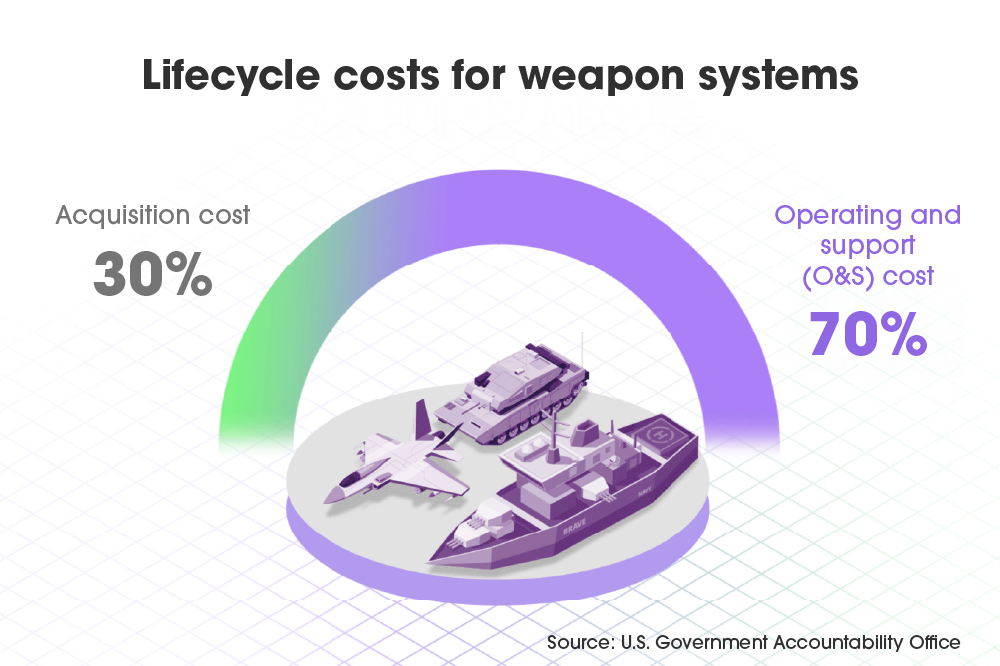
Weapons systems have a typical operational life of 20 to 40 years and require continuous maintenance and performance improvement throughout that lifecycle. The acquisition price of weapons and equipment accounts for only about 30% of the operating costs, with operating and support costs accounting for the other 70%. That level of investment in upkeep alone is why MRO is so crucial to the defense industry, but its importance goes beyond that — it also brings strategic and technological benefits.
MRO provides the opportunity to respond to changing battlefield conditions by improving the performance of existing weapon systems and adapting them to the latest technologies. In this feature, we will explain current trends in the MRO industry and discuss the ways in which it has become an indispensable strategic element in safeguarding futures.
The growing importance of MRO at sea
As MRO offers more than an alternative to costly asset replacement, governments are increasingly leveraging it to upgrade existing naval fleets with cutting-edge systems while reinforcing their defense posture. The global naval MRO market is growing as a result, with research company Mordor Intelligence predicting that it will increase from $59.48 billion in 2025 to $65.96 billion in 2030.
One underlying reason for this growth is the emergence of forward sustainment — bringing MRO operations closer to active theaters — as a priority in operational readiness strategies. The Asan Institute for Policy Studies states that by bringing MRO operations closer to active theaters, turnaround time is shortened, and mission availability is enhanced. As forward sustainment supports a more distributed, agile defense presence that can quickly adapt to evolving regional demands, governments have increasingly placed more emphasis on this approach in the upkeep of their fleets.
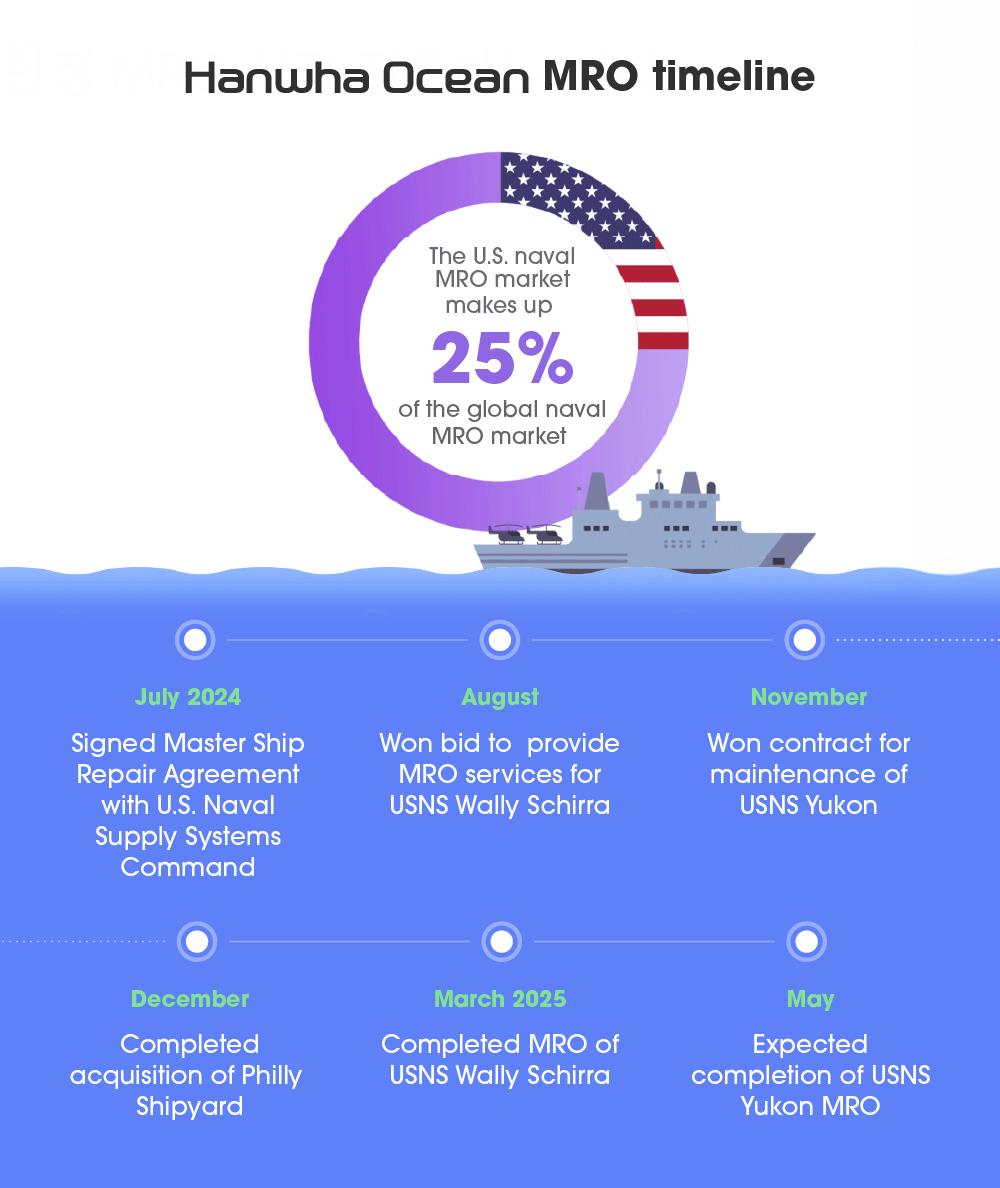
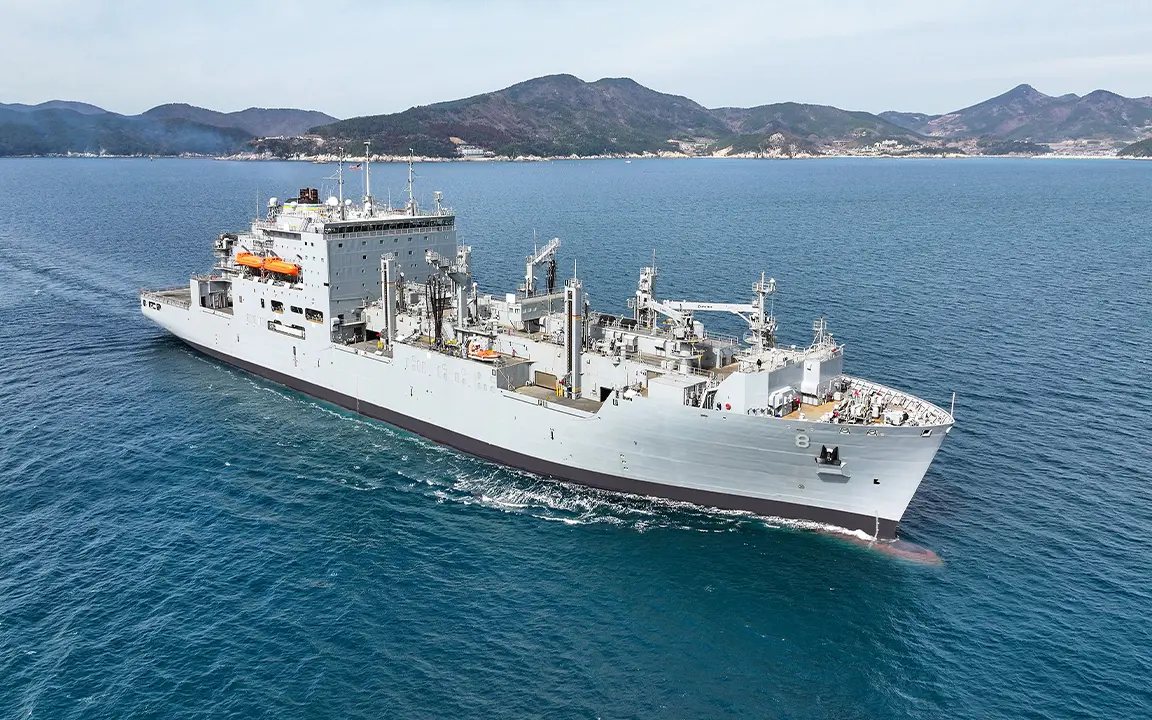
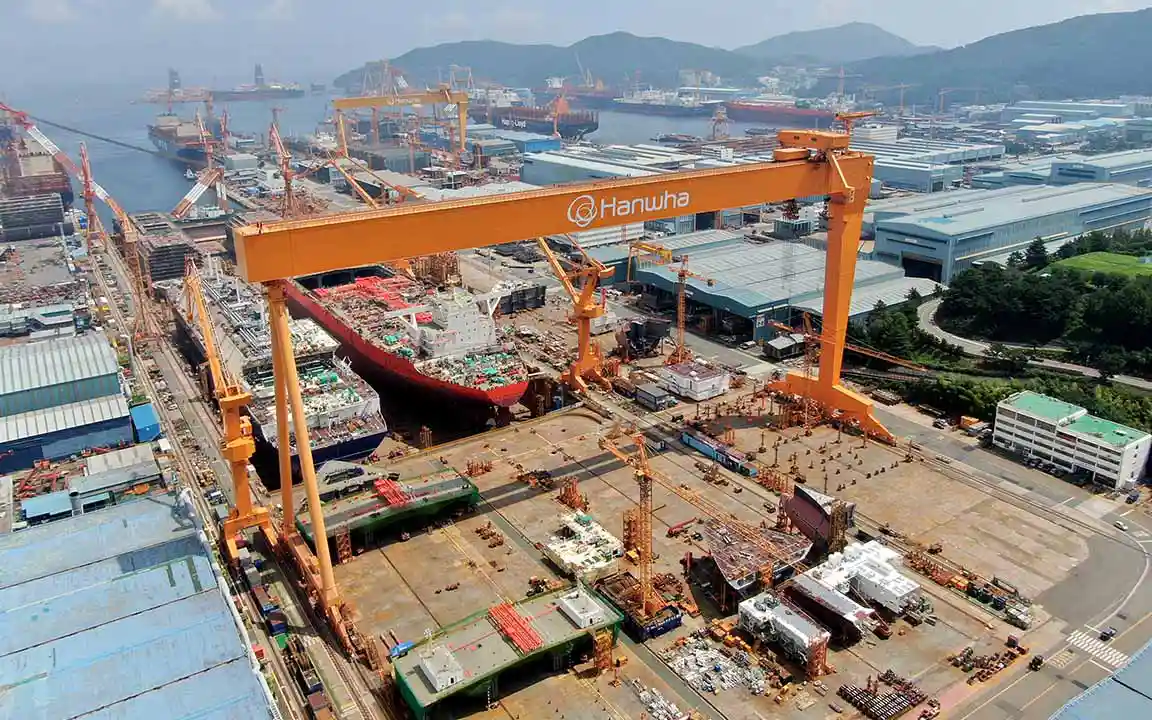
As a trusted partner in the shipbuilding industry, Hanwha has been actively pursuing ship MRO activities. In July 2024, it signed a five-year Master Ship Repair Agreement (MSRA) with the U.S. Naval Supply Systems Command, which validates the quality of Hanwha Ocean’s shipbuilding and MRO capabilities. After becoming the only South Korean shipbuilder to have won contracts with the U.S. Navy, Hanwha Ocean successfully completed MRO of USNS Wally Schirra, a 40,000-ton U.S. Navy dry cargo and ammunition ship, at Hanwha Ocean’s Geoje Shipyard in March 2025. The MRO of another vessel, the U.S. Navy’s 7th Fleet oiler USNS Yukon, is expected to conclude in May 2025.
Hanwha Ocean and Hanwha Systems also acquired Philly Shipyard in the U.S. in December 2024 and launched Hanwha Philly Shipyard. This will lead to an increase in shipbuilding capacity, modernization of the shipyard, and investment in workforce expansion and development. Reflecting Hanwha’s commitment to its partners, Hanwha Philly Shipyard aims to support the U.S. Navy’s pressing shipbuilding and repair needs in the long term.

Bolstering ground and air capabilities
A shifting global diplomatic and security environment that has increased the importance of collaboration between allied nations has also had an impact on ground and air MRO activities. With this in mind, Hanwha is engaging in a variety of localization efforts that strengthen bonds between South Korea and its allies while creating jobs and supporting local industries.
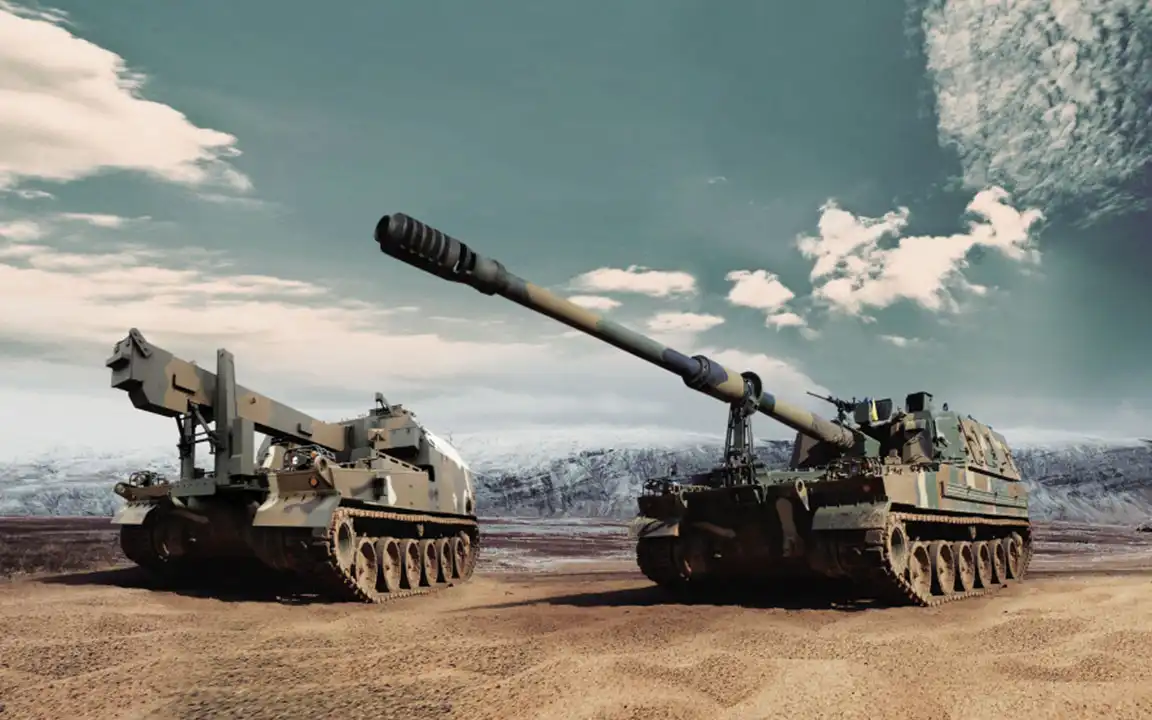
Hanwha Aerospace is expanding its MRO activities to include such localization efforts, recently signing a joint venture agreement with Poland’s WB Group to manufacture guided missiles for the Chunmoo multiple launch rocket system (MLRS) in Poland. This is the latest venture in Hanwha’s localization efforts, with another key agreement being the $1 billion contract signed with Romania in July 2024 to supply K9 self-propelled howitzers (SPH) and K10 ammunition resupply vehicles (ARV). Most of these weapons systems will be produced in Romania through localization programs that include local production of defense equipment, technology transfer, and local facilities for MRO.
This agreement comes in addition to the completion of the Hanwha Armoured Vehicle Centre of Excellence (H-ACE) in Geelong, Australia. The facility, which is the first overseas production base established by a Korean defense company, will produce AS9 SPHs and the AS10 armored ARV, as well as the Redback infantry fighting vehicle (IFV).
Additionally, Hanwha Aerospace has been a partner of the Republic of Korea (ROK) Air Force for more than 45 years. In this time, the company has produced over 10,000 engines for fighter jets, helicopters, naval vessels, and guided weapons, while also performing MRO on over 5,700 aircraft engines. Looking forward, Hanwha’s aircraft activities extend beyond MRO capabilities to align with its aims to produce advanced aero-engines entirely with its own technology.
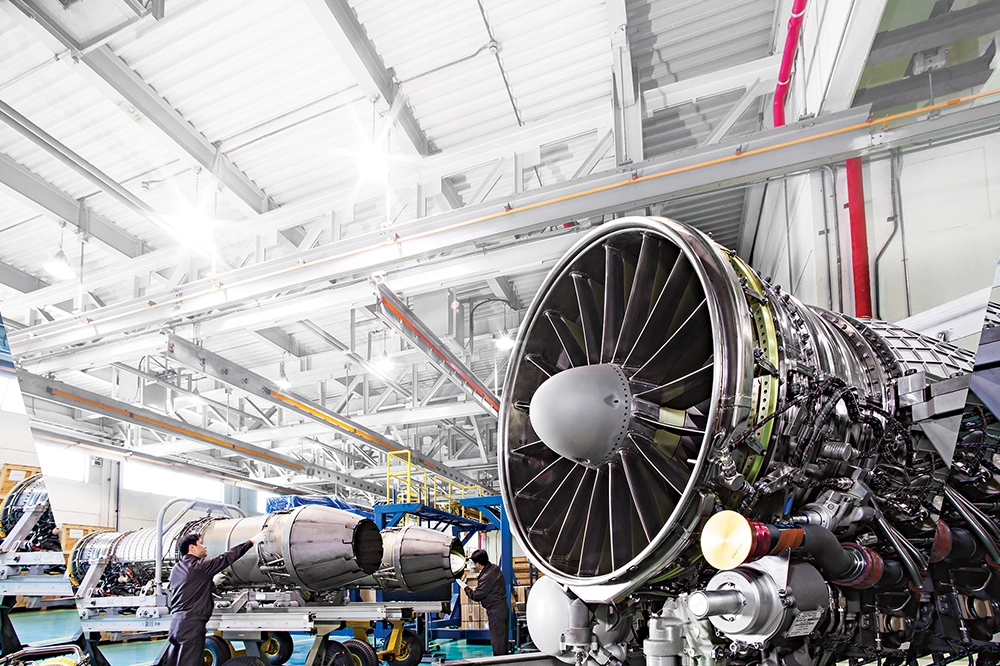

Workers assembling aero-engines at Hanwha Aerospace’s Changwon facility
Driving global readiness and resilience
With armament modernization a strategic priority, MRO is taking on new importance not only as a forward-looking capability that extends the operational life of weapons systems and maximizes cost efficiency beyond simple maintenance, but as an integral piece of nations’ defense postures in the modern geopolitical landscape.
By integrating next-generation technologies and strengthening global industrial partnerships, Hanwha is reinforcing its role as a trusted partner in the defense sector. With MRO facilities and expertise providing cutting-edge, integrated systems on land, at sea, and in the air, Hanwha continues to play a facilitating role as societies maximize defense readiness.
Get the latest news about Hanwha, right in your inbox.
Fields marked with * are mandatory.
- Non-employee
- Employee







