Building resilience: How supply chains, technology, and strategic flexibility strengthen energy security

Energy security is more critical than ever as rising demand, geopolitical uncertainties, and supply chain disruptions challenge the reliability of global energy systems. Nations and industries must adapt to these shifts by securing stable, flexible, and cost-effective energy sources.
CERAWeek 2025, the “Super Bowl of energy,” brings together over 10,000 participants from 80 countries in Houston, Texas, U.S. from March 10 to 14 to address the most pressing challenges in energy resilience, supply chain stability, and the role of emerging technologies. With shifting policies and evolving energy solutions, discussions will focus on how industries can navigate an increasingly complex landscape.
Ensuring a secure energy future requires strategic investments in infrastructure, fuel diversity, and digital transformation. A balanced energy mix, stronger supply chains, and cutting-edge technology will be key to maintaining long-term reliability in a rapidly changing world.
The evolving energy landscape
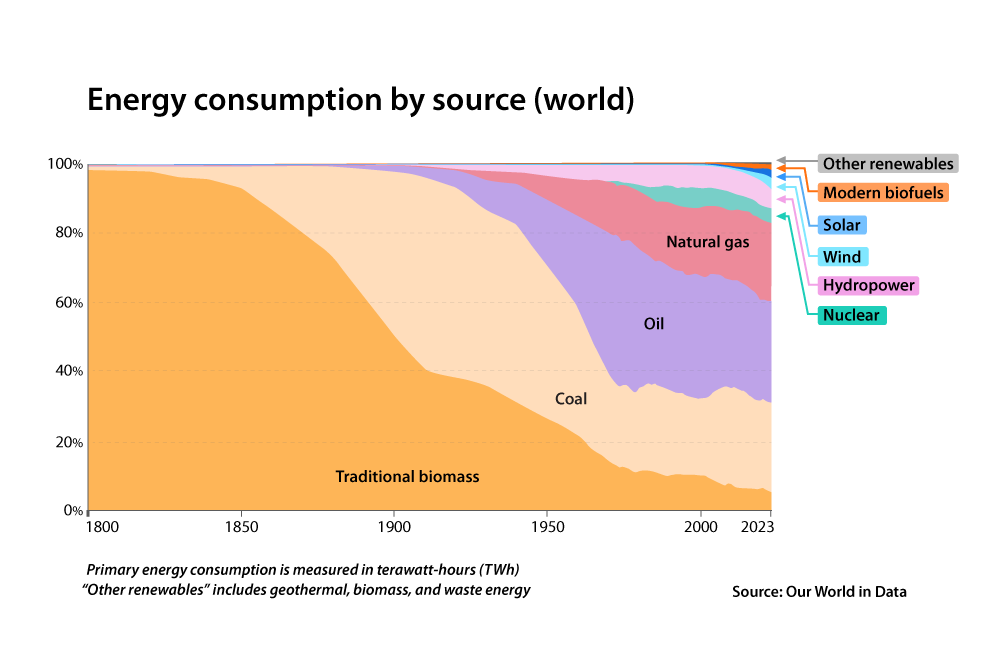
The way energy is produced, distributed, and consumed is undergoing a major transformation. Nations are rethinking their energy strategies, integrating a broader mix of renewables, conventional fuels, and emerging technologies to enhance long-term security. This shift is being driven by rising demand, evolving policies, and geopolitical uncertainties, forcing industries to adapt to new energy dynamics while ensuring stability and affordability.
Heavy reliance on a single energy source leaves nations vulnerable to disruptions and price volatility. A diverse energy mix provides strategic flexibility and is key to resilience. By integrating renewables, lower-carbon conventional fuels like liquefied natural gas (LNG), hydrogen, and advanced grid solutions, countries can reduce risk, enhance flexibility, and maintain energy stability in an unpredictable world.
However, energy security does not depend on fuel diversity alone — the infrastructure and systems that support energy production and distribution must be equally resilient. Ensuring stable access to energy requires strong supply chains and continuous innovation.
Supply chains: The backbone of a resilient energy ecosystem
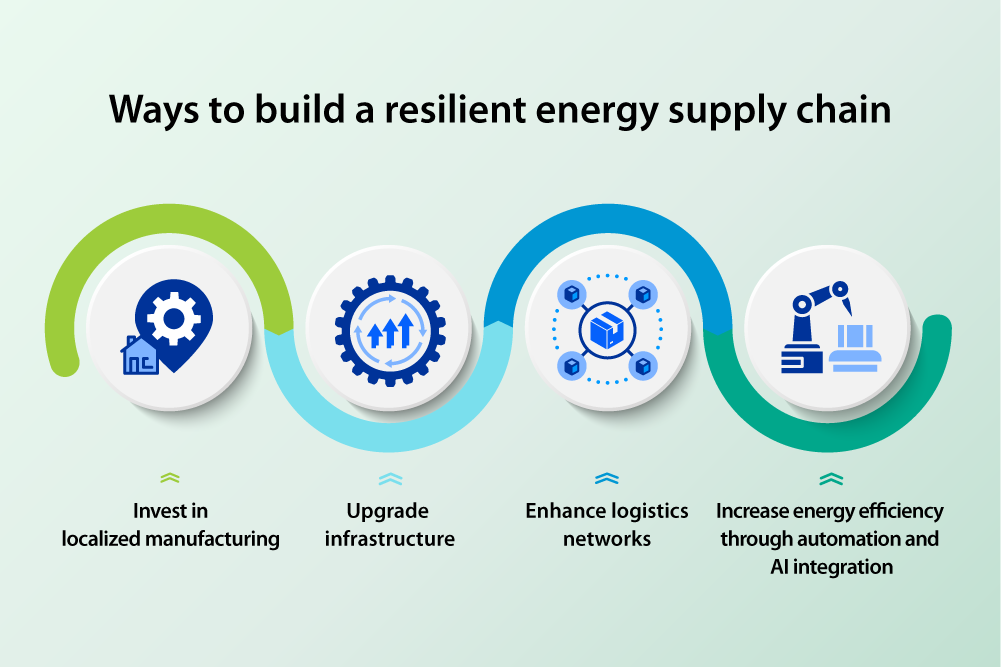
A resilient energy supply chain is not just a response to disruptions — it is a proactive strategy for securing global energy stability. Ensuring a steady flow of materials, components, and infrastructure is critical to preventing shortages, price fluctuations, and supply delays.
However, global energy supply chains face increasing challenges. Trade policies, material shortages, and geopolitical tensions have exposed vulnerabilities in sourcing critical energy components. Many industries depend on materials that are only available in a few regions, which can create bottlenecks and disrupt production. A supply chain is only as strong as its weakest link — without robust infrastructure, even the most advanced energy technologies cannot be deployed at scale.
To strengthen supply networks, investment in localized production, infrastructure upgrades, and streamlining operations is essential. Expanding manufacturing capabilities improves efficiency and stability while ensuring a more resilient energy system. Digital tracking systems and advanced logistics solutions are streamlining supply chain management by enhancing visibility, optimizing distribution, and enabling real-time decision-making.
Hanwha is investing heavily to reinforce energy supply chains and strengthen infrastructure. Its $2.5 billion Solar Hub will increase U.S. solar production capacity to 8.4 gigawatts — enough to power 1.3 million homes annually — making Hanwha the only company in North America producing all key components of the solar supply chain domestically. Investments like these play a crucial role in enhancing energy security by reducing supply vulnerabilities and ensuring a more stable energy future.

The role of technology and innovation in securing energy supply
A secure supply chain alone cannot guarantee a robust energy system. Continued technological innovation is essential to modernizing grids, integrating diverse energy sources, and ensuring flexibility in fuel use. As energy networks become more complex, nations must invest in AI-driven management, energy storage solutions, and advanced infrastructure to maintain a reliable and adaptable energy supply.
Beyond supply and infrastructure, energy efficiency is fundamental to long-term stability. Maximizing output while minimizing waste allows energy systems to generate more power using the same or fewer resources, reducing dependence on external suppliers and improving supply chain resilience.
AI and energy storage systems (ESS) are at the heart of grid strength. AI-driven energy management optimizes power distribution, predicts demand fluctuations, and improves overall system efficiency — reducing costs while preventing shortages. Meanwhile, ESS play a crucial role in stabilizing electricity grids by storing excess power and releasing it during peak demand, ensuring reliability even amid supply fluctuations. Hanwha is investing in several large-scale ESS projects to support the integration of renewable energy sources and enhance grid capacity, ensuring a more resilient and reliable energy supply.
One of the most promising advancements in energy efficiency is perovskite tandem cells, which significantly enhance solar energy conversion. Hanwha Qcells has set a world record efficiency of 28.6% on a full-area M10-sized perovskite-silicon tandem cell, marking a major leap forward in moving perovskite tandem cells from theoretical, lab-only achievements to real-world applications. This milestone paves the way for commercialization and broader adoption, making high-efficiency solar technology more viable for large-scale energy generation.
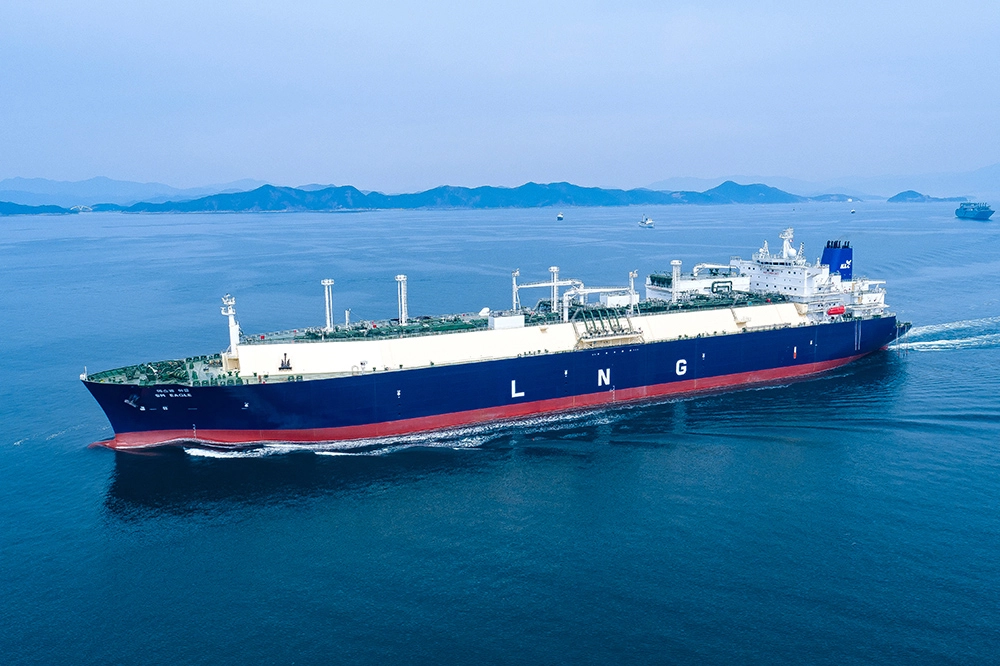

Hanwha Ocean's LNG carrier at sea
Beyond advancements in solar efficiency, technological innovation is also driving a more stable and adaptable energy mix. Diverse energy sources play a critical role in ensuring reliability as energy needs evolve.
Consequently, LNG demand is rising as industries seek lower-emission alternatives to coal and oil. Its flexibility and ability to deliver stable, on-demand power make it an increasingly critical part of the global energy transition. As nations diversify their energy mix and reduce reliance on higher-emitting fuels, LNG is expected to play a growing role in ensuring grid stability and supporting industrial energy needs.
Hanwha is building out its LNG value chain across production, storage, transport, and power generation, enhancing supply chain durability and optimizing energy transportation. As of February 2025, Hanwha Ocean holds the highest number of LNG carrier orders worldwide, reinforcing its capacity to support energy transportation. The delivery of its 200th LNG carrier underscores Hanwha Ocean’s technological leadership in LNG shipping and its role in reducing emissions across the energy value chain. By integrating dual-fuel engines, smart ship technology, and other carbon-reducing innovations, Hanwha is improving transport efficiency and reliability while ensuring LNG remains a secure and adaptable energy source.
As the global energy landscape evolves, securing a stable, flexible, and cost-effective energy supply is more urgent than ever. Rising demand, geopolitical uncertainties, and supply chain challenges require strategic investment in infrastructure, fuel diversity, and technology to maintain long-term security. Hanwha is contributing to a more secure energy ecosystem by leveraging its expertise across the entire energy value chain — from production to storage, transport, and utilization — to develop solutions that strengthen energy resilience and meet industry demands.
Get the latest news about Hanwha, right in your inbox.
Fields marked with * are mandatory.
- Non-employee
- Employee