Manufacturing trends for 2025: AI, automation, supply chains, and energy

As 2025 unfolds, manufacturing is evolving amid numerous global challenges. Geopolitical tensions, climate concerns, and shifts in energy systems are catalyzing industrial transformation, while the Fourth Industrial Revolution continues to advance through automation, AI, and digital connectivity. These forces are reshaping how manufacturers optimize production, manage supply chains, and adapt to new economic realities.
Against this backdrop, four key trends are set to define the manufacturing landscape in 2025: AI integration, industrial automation, localized supply chains, and the energy demands of AI-driven data centers. How will these trends shape the future of manufacturing, and what impact will they have on industries worldwide?
1. The growing role of AI in manufacturing
AI is no longer just an emerging technology in manufacturing — it is becoming the backbone of factories, reshaping how products are made, how supply chains operate, and how workplaces stay safe. With 89% of manufacturers planning to integrate AI into their production networks, its impact is undeniable.
One of AI’s most beneficial capabilities within factories is computer vision, which enables real-time defect detection. Instead of relying solely on human inspectors, AI-powered systems scan products in milliseconds, flagging even the smallest imperfections before they leave the production line.
Predictive maintenance is also revolutionizing factory floors, shifting maintenance from a rigid schedule to a data-driven strategy. By analyzing machine performance, AI helps manufacturers anticipate failures, reduce downtime, and cut costs, keeping production lines running smoothly.
AI is also refining and optimizing global supply chain management, optimizing logistics, procurement, and inventory, ensuring raw materials and finished goods move efficiently. By reducing shortages, speeding up delivery times, and improving distribution networks, AI is helping manufacturers build more resilient and adaptive supply chains.
AI is not just making production smarter — it is also making factories safer for workers by detecting hazards and ensuring compliance with safety protocols. Hanwha Vision’s smart factory solutions integrate AI-powered surveillance cameras to monitor forklift operations, addressing a serious safety concern — forklift accidents in the U.S. cause between 75 and 95 deaths annually and 8,000 to 9,000 serious injuries requiring time away from work. By issuing real-time alerts and using proximity detection, this AI-powered system helps prevent collisions and improve workplace safety.
As AI adoption accelerates, manufacturing will continue to evolve, improving efficiency not only in production but also across logistics, infrastructure, and energy sectors. The factories of 2025 won’t just be smarter — they will be faster, safer, and more efficient than ever before.
2. Increasing automation in factories and shipyards
While AI enhances decision-making and adaptability, automation is redefining execution. AI enables machines to analyze data and adjust processes dynamically, while automation focuses on predefined tasks, reducing manual intervention and maximizing efficiency. But when AI and automation work together, the impact is transformative.
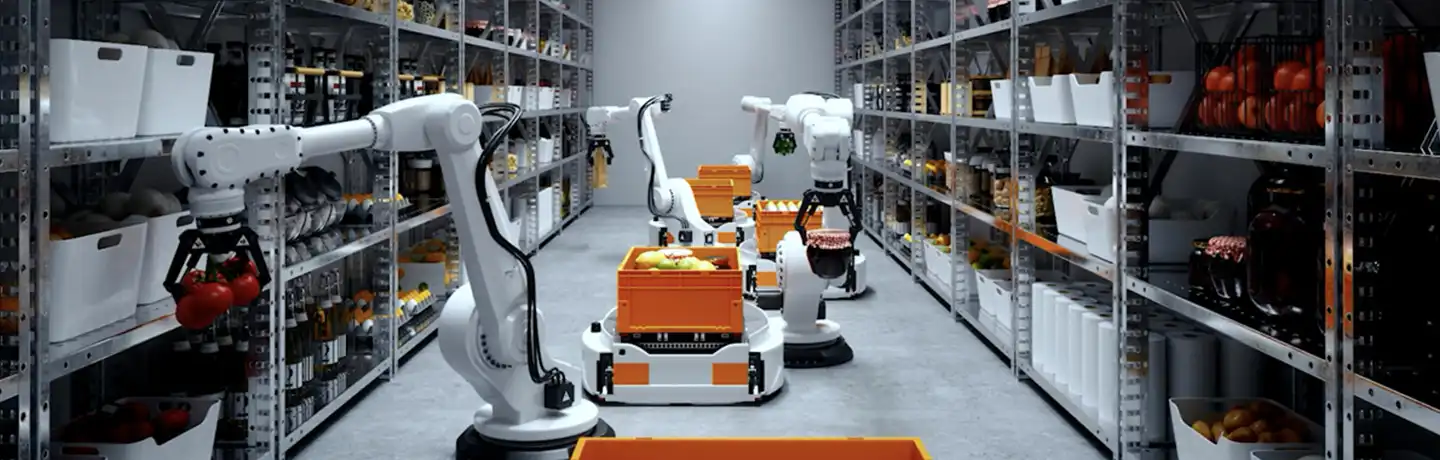
In smart factories and shipyards, automation is streamlining production, enhancing precision, and reducing human workload. In smart manufacturing, real-time data, AI, and robotic process automation create interconnected production systems, optimizing workflows and minimizing errors. Meanwhile, shipyards are integrating automation into welding, painting, and inspection, increasing efficiency and worker safety in hazardous environments.
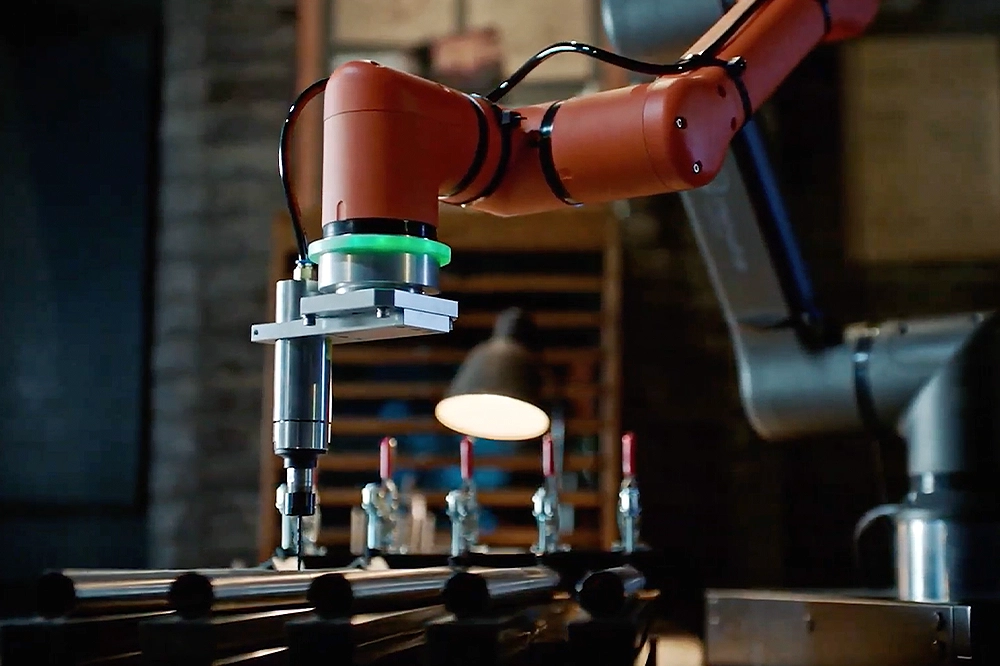
An important factor in this shift is collaborative robots (cobots), which differ from traditional industrial robots that require protective cages for safety. Cobots are designed to work alongside humans, with built-in safety features such as force-limiting sensors and real-time responsiveness that allow them to operate safely in shared workspaces.
Cobots are already automating physically demanding and repetitive tasks, including component assembly, quality inspection, machine tending, and palletizing. In manufacturing, they are ensuring greater precision, consistency, and efficiency while reducing human exposure to hazardous conditions.
As cobots play a growing role in industrial automation, Hanwha Robotics’ HCR cobot series is accelerating their adoption across industries, boosting productivity and cost efficiency. In shipbuilding, Hanwha Ocean is deploying cobots at its Geoje shipyard to assist with high-risk tasks like welding and painting, improving worker safety and production consistency. These cobots aid in improving digital twin technology by providing data that can be used for process optimization and predictive maintenance.
3. The shift toward localized supply chains
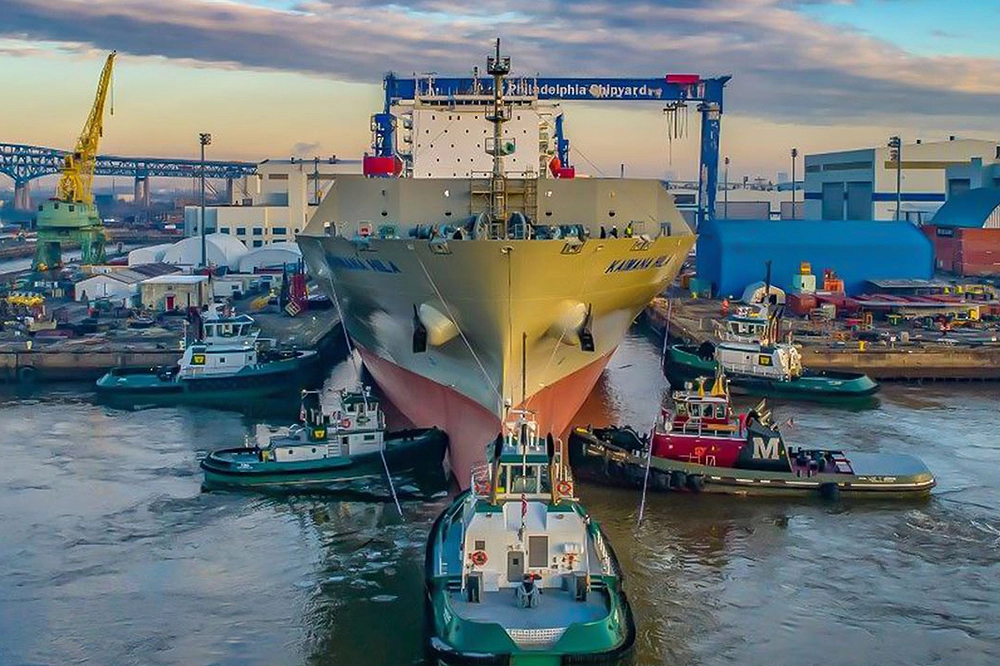

While automation and AI are reshaping how goods are produced, manufacturers are also rethinking where production happens. In 2025, reshoring and nearshoring are accelerating as companies work to strengthen supply chain resilience and reduce reliance on distant suppliers. The COVID-19 pandemic exposed critical weaknesses in global logistics, forcing businesses to rethink their sourcing strategies. Now, geopolitical tensions and shifting trade policies are further driving this transition.
Beyond reducing supply chain disruptions, nearshoring offers a range of benefits. By keeping production closer to demand, manufacturers can respond more quickly to market shifts, improving flexibility and operational agility. Strengthening domestic industries also brings economic advantages, creating jobs and fueling local investment.
With improved quality control, lower shipping costs, and faster delivery times, companies can build supply chains that are not only more efficient but also more resilient in an unpredictable global market.
Recognizing these benefits, Hanwha Qcells is expanding U.S. manufacturing and reinforcing domestic supply chains with the construction of the Solar Hub, an integrated solar power production complex in the U.S., being a key example. Additionally, to expand U.S. shipbuilding capacity and further strengthen supply chain resilience, Hanwha has acquired Philly Shipyard, which is now operating as Hanwha Philly Shipyard. These strategic investments support local economies and provide greater stability in an increasingly unpredictable global market.
4. Managing AI’s rising power needs
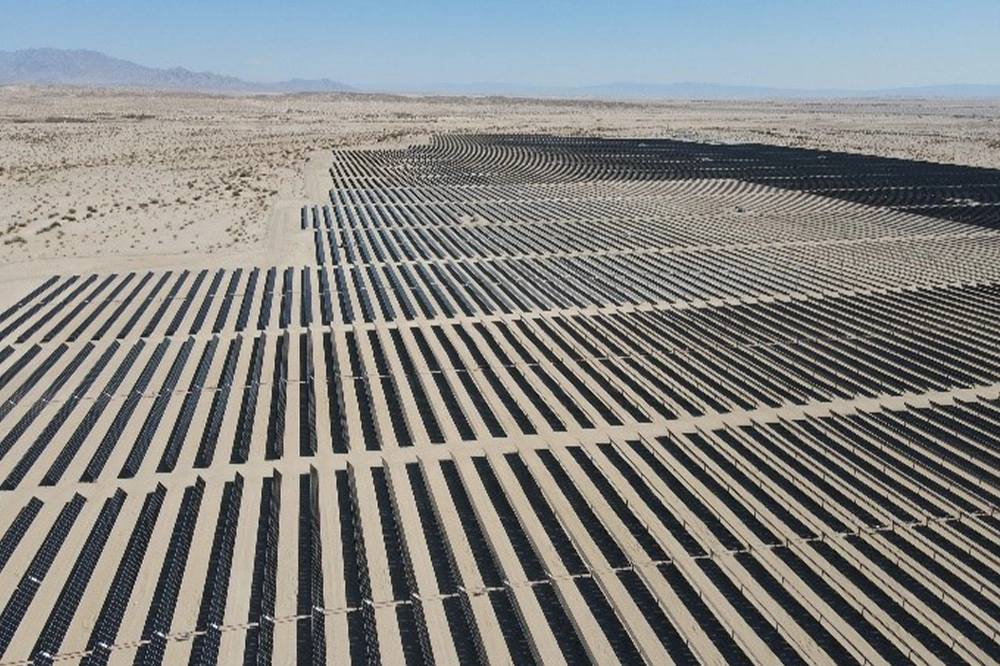

The final trend shaping manufacturing in 2025 is the rising energy demand of AI-driven data centers, which is putting unprecedented pressure on power grids and accelerating the need for clean power solutions. Data centers are projected to consume as much electricity as entire cities, with a study by EPRI estimating they could account for up to 9% of total U.S. electricity generation by 2030 — posing a major challenge for regional power infrastructure.
To keep up with demand while minimizing environmental impact, data centers are turning to renewable energy and advanced storage solutions. Solar, wind, and battery storage technologies are being integrated to provide stable, reliable power, ensuring these energy-intensive facilities can operate efficiently while minimizing environmental impact.
Amid the accelerating energy transition, Hanwha has been forging alliances with global companies, helping them reach their net zero goals. Through partnerships with Meta and Microsoft, Hanwha Qcells is delivering solar power and energy storage solutions, supporting tech companies as they work to transition their operations to being powered in part by renewable energy. As the private sector's demand for renewable energy continues to grow, Hanwha Qcells is helping to decarbonize the grid and diversify the clean energy global supply chain.
Get the latest news about Hanwha, right in your inbox.
Fields marked with * are mandatory.
- Non-employee
- Employee











